Health
Bacterial Skin Rash – Causes, Remedies, And Treatments Revealed!
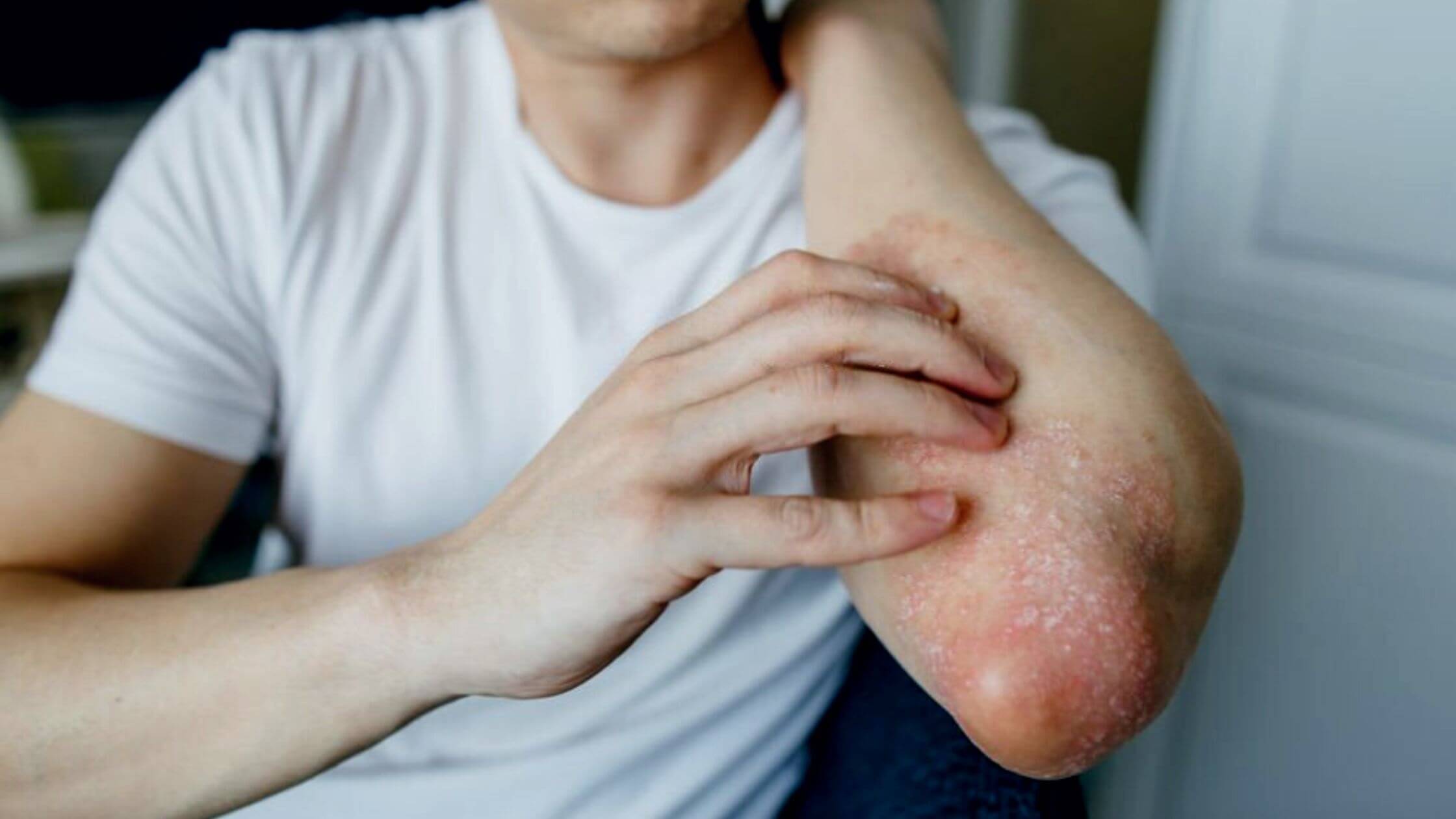
In the human body, the skin is the biggest organ. It functions as a protective layer around our body. Sometimes the skin itself becomes infected. Skin Rash can be caused by a wide variety of germs, and the symptoms can vary from mild to serious. Mild infections may be treatable with easily accessible medications and home remedies.
But serious skin conditions require proper medical attention. A rash is a condition in which human skin changes its color, appearance, or texture. A rash may be localized in one part of the body or affect all the skin. Rashes can lead the skin to change color and texture. It can be itchy, warm, dry, chapped, cracked, and may be painful.
What Are The Various Infections That Cause Bacterial Skin Rash?
The main cause of rashes is dermatitis, which is when your skin reacts to allergens or irritants. Skin rashes can be caused by bacteria, viruses, allergens, and conditions including eczema, hives, and psoriasis. There are different types of treatments that can relieve the symptoms and get rid of the rash.
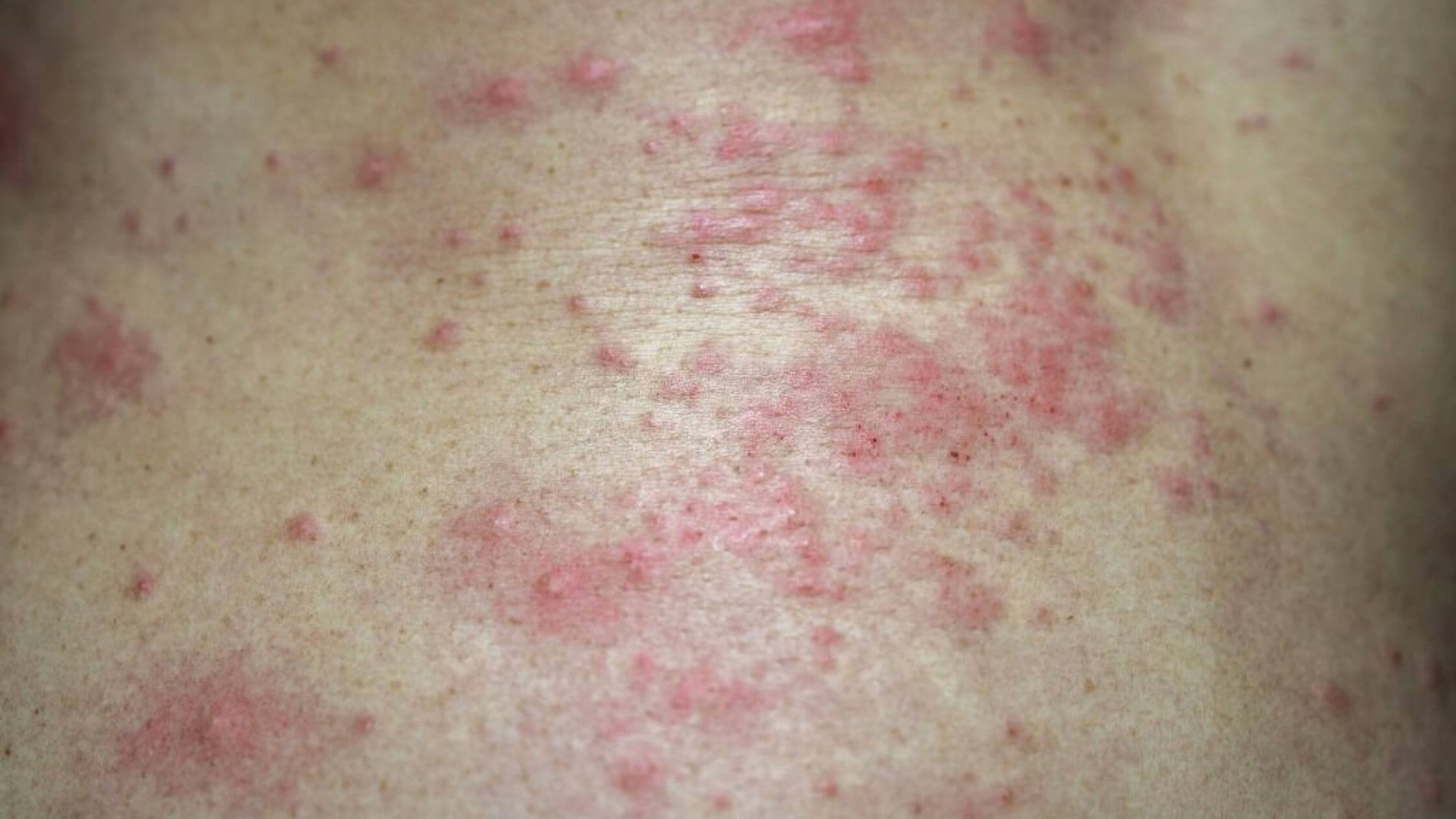
Skin rashes are very common, and everyone envelope at least one skin rash during their lifetime. It is extremely common to sometimes feel itchy or have red, bumpy skin for a little while. Everyone regardless of age can get infected by skin rashes. Infants can be infected by diaper rash and cradle caps. Older kids or adults can develop contact dermatitis as skin becomes more sensitive to allergens or irritants over time.
Bacteria cause numerous types of skin rashes. The severity of bacterial infections can range from mild to life-threatening. Most infections are caused by Staphylococcus aureus (often referred to as staph infection) or Streptococcus pyogenes, which is the same bacteria responsible for strep throat. The infections generally start when the skin is irritated or disrupted, such as by a cut, scrape, puncture, or rash.
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the affected region of the skin. It affects the two deepest layers of the skin, called the dermis and subcutaneous tissue. The condition often appears as a swollen red area of skin and often feels tender and hot when touched.
Cellulitis infects, usually when skin is broken, such as near bruises, ulcers, burns, or surgical wounds. Different types of bacteria can cause this condition. The most common bacteria that cause cellulitis are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. Cellulitis can be dangerous if it spreads to your bloodstream.
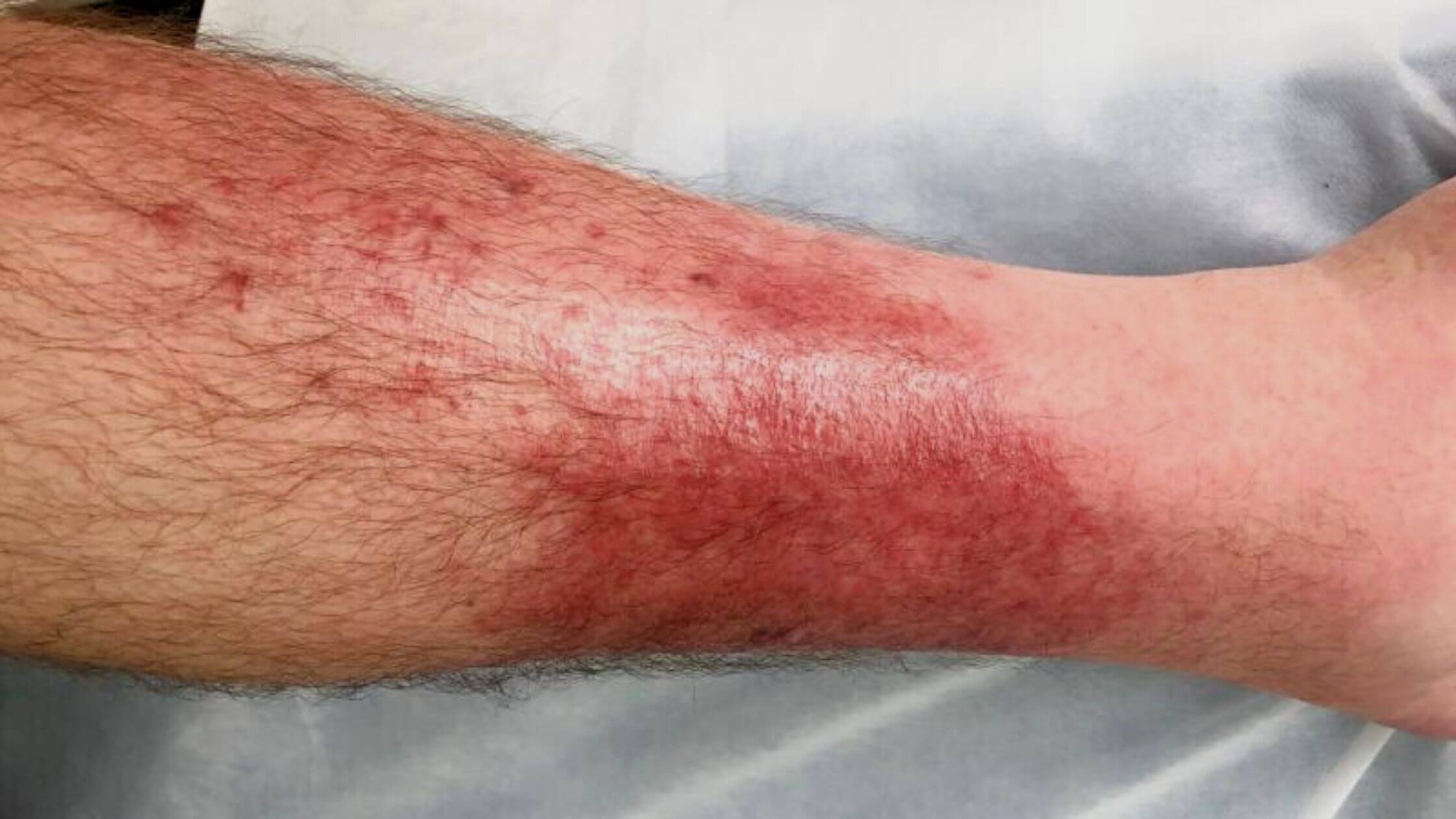
It can lead to developing symptoms of septicemia like high fever, chills, vomiting, rapid heart rate, etc. Immediate emergency care is required if symptoms like these develop. Doctors normally diagnose this condition by doing a physical examination and looking at the affected parts of the skin. There is no need for blood tests or other lab tests. Treatment of cellulitis involves antibiotics.
Most types of cellulitis infections can be treated with antibiotics that can be taken orally. More serious infections may need to be treated in the hospital with intravenous antibiotics, which are given directly into the vein. If the cellulitis infection is in the arm or leg, then keeping that limb elevated can help decrease swelling and speed up recovery.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is a form of cellulitis, but unlike cellulitis, which affects deeper tissues in the skin, erysipelas only affects the upper layers. However, the two conditions can overlap in their symptoms, making it difficult for physicians to differentiate between the two conditions.
Earlier it was thought that it affected only the face, but now it is estimated that around 80 percent of cases affect the legs. Arms and torso are also infected. Numerous symptoms like fevers, chills, shivering, and high temperature can occur before any visible signs of erysipelas appear on the skin.
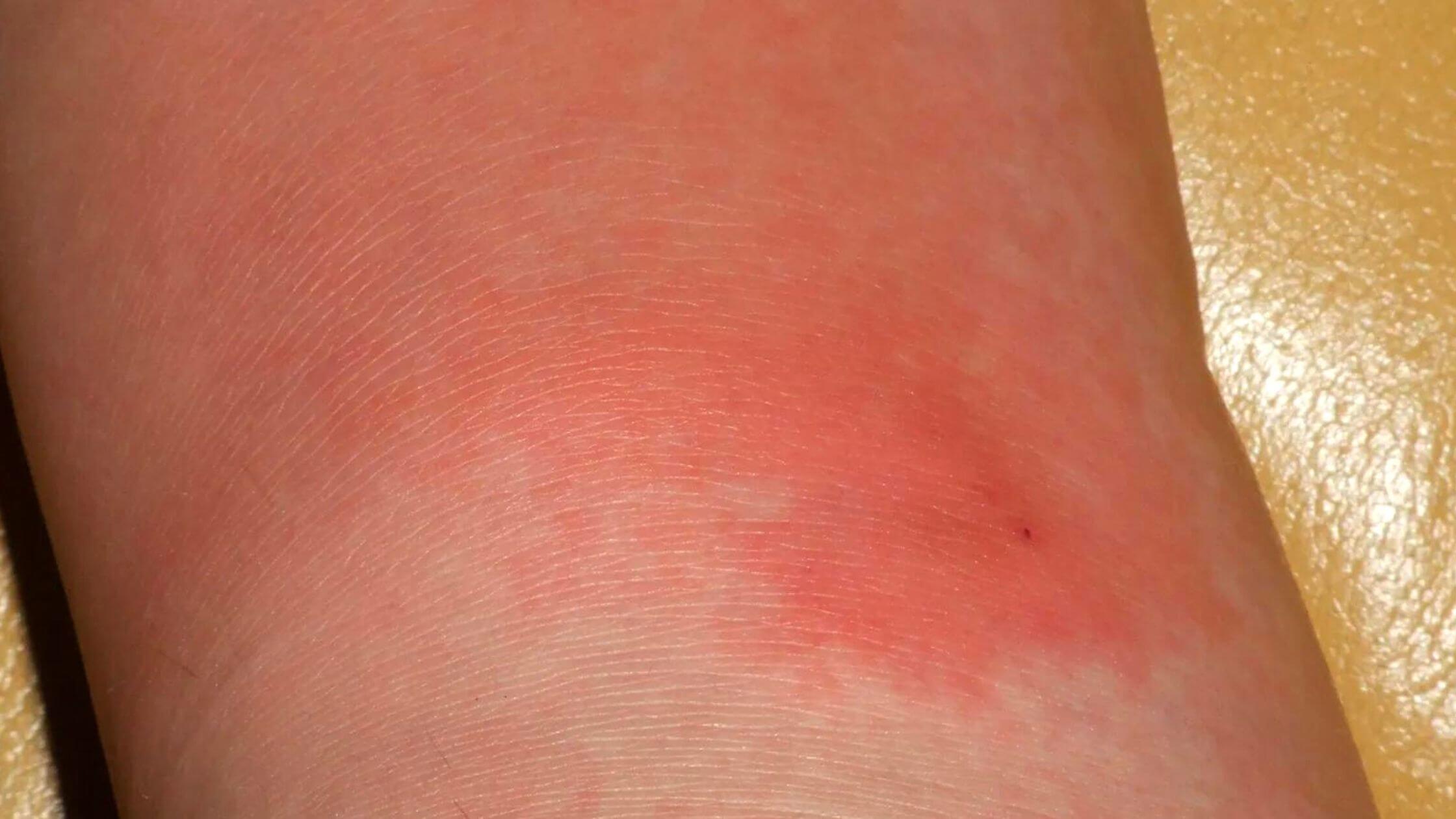
Skin can appear swollen, shiny, red, and warm. Skin can turn purple or black in severe cases. Erysipelas can be caused by injuries to the skin such as cuts, ulcers, and insect or animal bites. Doctors will be able to diagnose this condition by the appearance and symptoms of the affected area. Erysipelas is a curable infection.
Antibiotics are used to treat erysipelas. Antibiotics used depends on the type of germs that infected the skin. Penicillin will be a common ingredient. Those who are allergic to penicillin are given erythromycin and cephalexin. Antibiotics are taken orally for one to two weeks.
If the condition is severe, then the drugs are administered directly into the vein. To prevent clotting, keep the infected area elevated. Cooling packs can be used to relieve pain and discomfort. Lotions are prescribed to prevent skin from getting dry and cracking.
Hot Tub Folliculitis
It is a skin infection by a bacterium called Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These bacteria are found in warm, moist environments like hot tubs and swimming pools. The bacteria can survive even in chlorinated water, making it very potent.
Hot tub rash looks like widespread itchy, red bumps. It can develop on any body part exposed to bacteria-infested water. This condition can develop on your face, chest, arms, buttocks, genitals, and legs. The most common symptom of hot tub rash is an itchy red rash, which comes with inflamed hair follicles. This can develop within a few days of coming in contact with a hot tub.
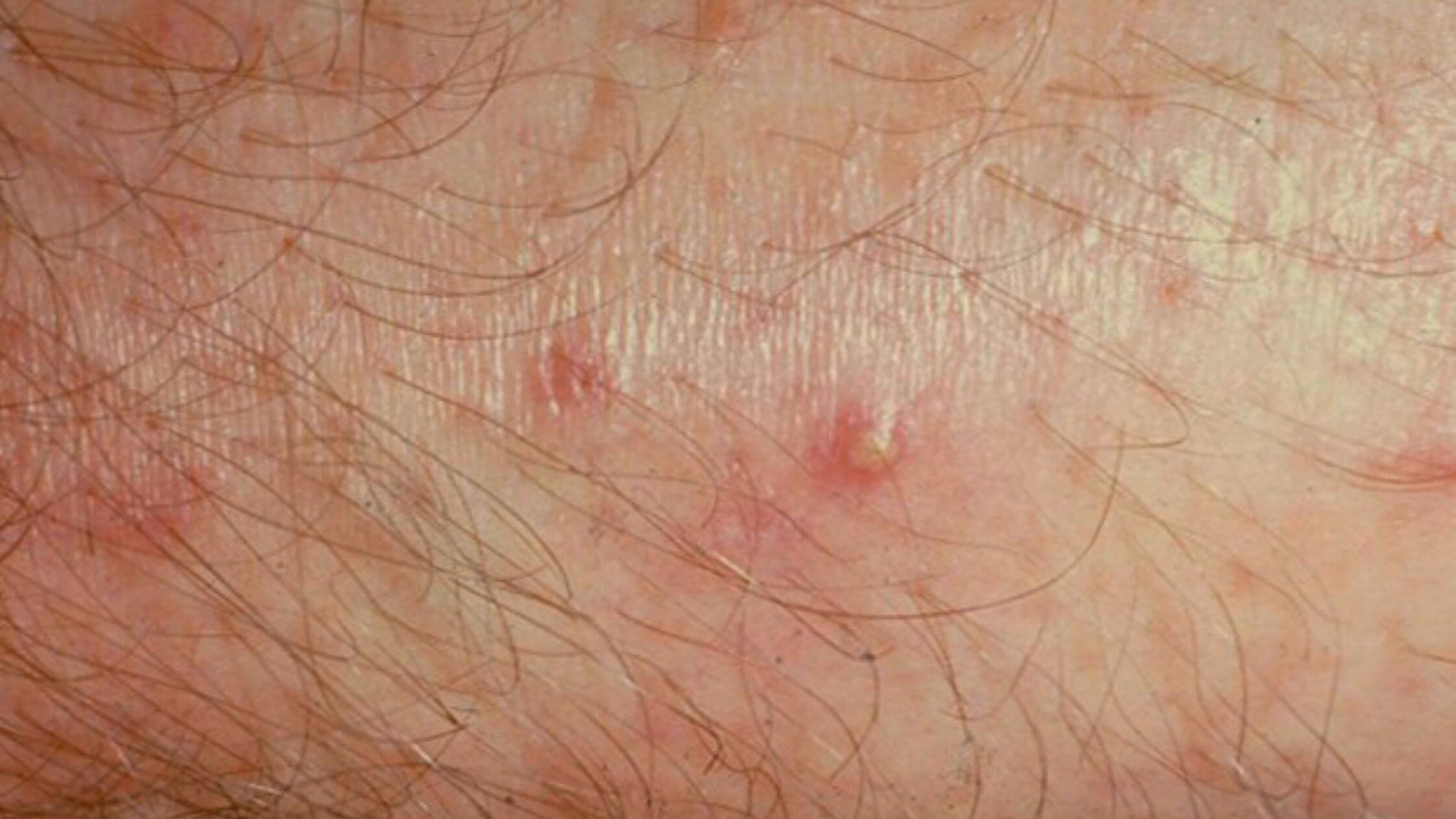
Other symptoms include diarrhea, eye pain, fever, headache, sore throat, nausea, and vomiting. Bumps on the skin may get filled with yellow or greenish-colored pus. Children are more prone to this condition because their skin is thinner.
Hot tub rash is diagnosed by a skin exam. There is no special diagnostic test for this condition. There is no specific treatment for hot tub folliculitis. It usually gets resolved within one or two weeks. Using a topical silver sulfadiazine cream will be beneficial. Contact your physician if it gets serious or takes a long time to heal.
Furuncles
A furuncle, which is often referred to as a boil, is a painful infection involving hair follicles and surrounding tissue. This infection can affect anywhere with hair growth. It most commonly appears on the face, neck, thigh, and buttocks.
The infected hair follicle will become inflamed. There will be a red, raised bump on your skin around the hair follicle. Cloudy pus comes out when it ruptures. The pus is a result of the body’s attempt to fight infection.
A furuncle may begin as a small pimple. But when the infection gets serious, the boil can become hard and painful. The size of a boil can reach to the size of over two inches. Scars may develop later. The common cause behind a furuncle is Staphylococcus aureus. So furuncles are called staph infections.
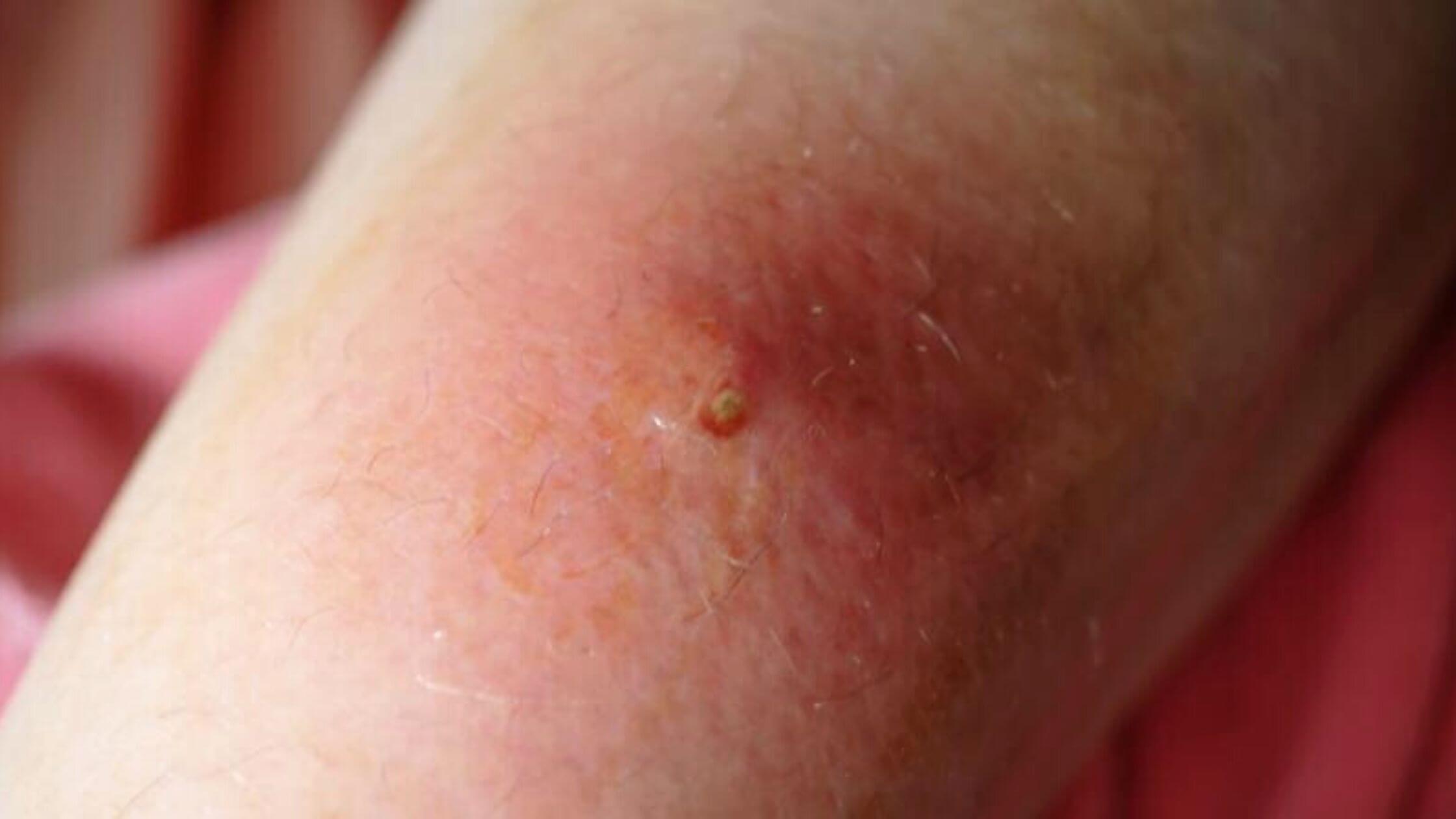
The bacteria can get inside if there occurs a break in the skin, such as a cut or scratch. Boils can get serious if you have a weak immune system or have a condition that slows down the healing of wounds. Diabetes and eczema are two examples of chronic conditions that may increase the risk of getting a staph infection.
The risk of getting an infection can also increase if there is close contact with a person having a staph infection. Furuncles usually heal by themselves. The pus will drain, and the infection will heal within a few days.
You will have to seek medical help if the boil remains large, unruptured, and painful for more than a week. The doctor will have to cut open the boil to drain it. It is followed by a course of antibiotics taken orally. In case of benign boils, warm compresses are used for rupturing a furuncle.
Impetigo
Impetigo is a bacterial infection affecting the epidermis. It is a highly contagious skin infection. It affects children more than adults. It is usually caused by Streptococcus bacteria. Impetigo is an itchy and painful skin infection. Impetigo usually infects children between the ages of 2 and 6. It also affects older children and adults.
There is a higher chance of getting infected if you live in a tropical climate and live in close, crowded conditions. Impetigo infection happens when the skin breaks due to a cut, bite, or scratch. Infection occurs when bacteria enter through the break in the skin.
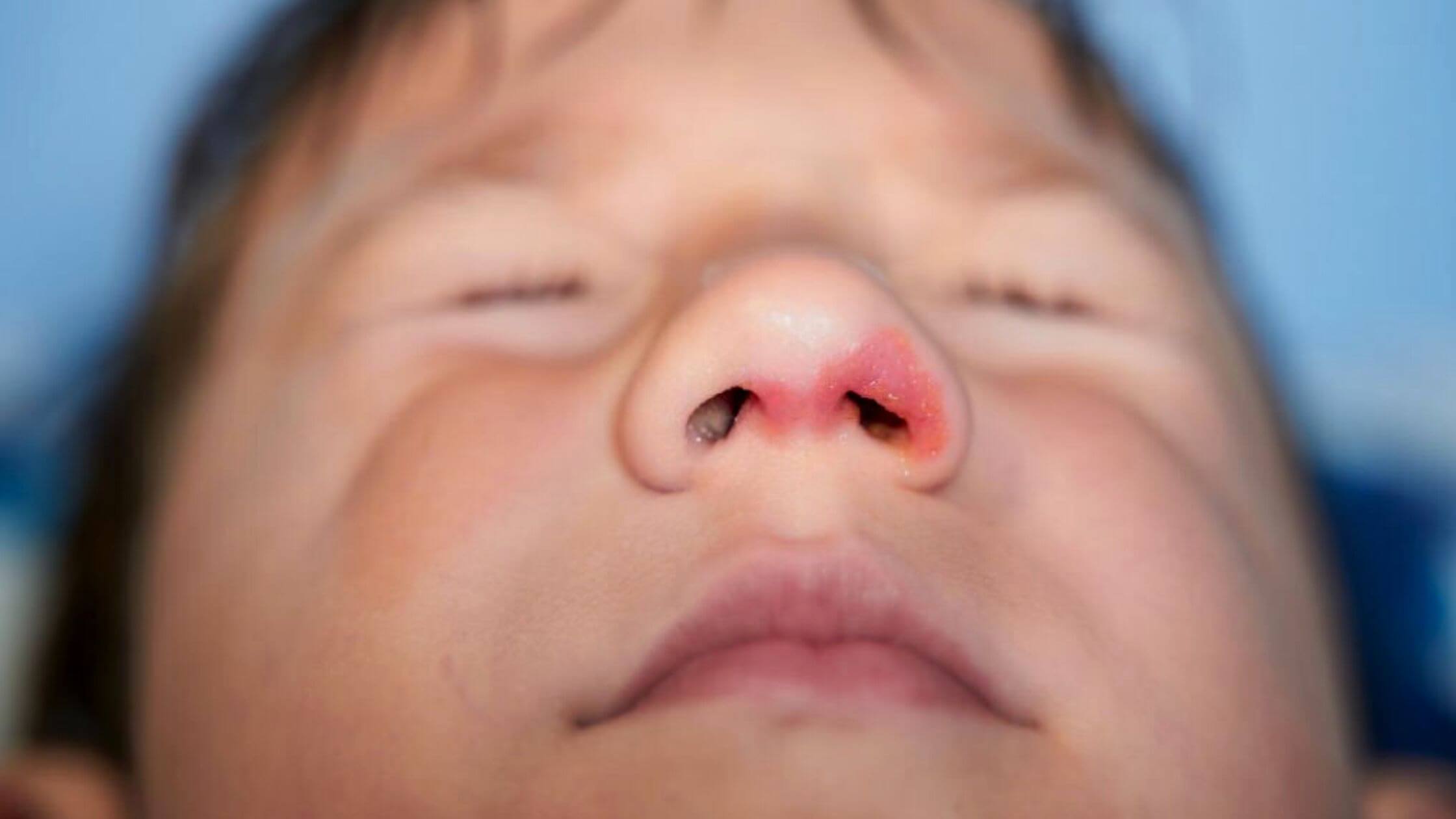
Impetigo can also happen to unbroken skin. Initial signs of impetigo include sores and blisters on the mouth and nose. Legs and arms are also infected. Impetigo is highly contagious. You can be infected with impetigo by coming in contact with sores or mucus or nasal discharge from an infected person. So it is advised not to share personal belongings such as towels and clothes.
Symptoms of impetigo include pus-filled blisters that will burst easily, a rash that spreads, and skin wounds on lips, nose, ears, arms, and legs. The blisters form scabs with yellow or brown crust. Impetigo is diagnosed based on how the sores look. The skin sample is sent to a laboratory and the bacteria causing the disease is figured out.
On the basis of the right diagnosis, a proper antibiotic is prescribed. Antibiotics are applied to the skin. If the condition covers a large part of the body, then oral medications are required. Impetigo often cures itself within about three weeks, even without treatment. Sometimes it takes longer.
Erythrasma
Erythrasma is a superficial skin infection caused by a bacterium known as Corynebacterium minutissimum. Erythrasma is a chronic or long-term skin condition. It usually develops in the skin folds. It is more prevalent in warm and humid tropical climates.
Common symptoms of erythrasma include pink, red, or brown skin patches with scales and mild itchy skin. There will also be wrinkling in the skin. Patches can be of different sizes. They begin as pink or red in color, then they become brown and scaly. The patches are commonly found in the groin area, armpits, or between toes.
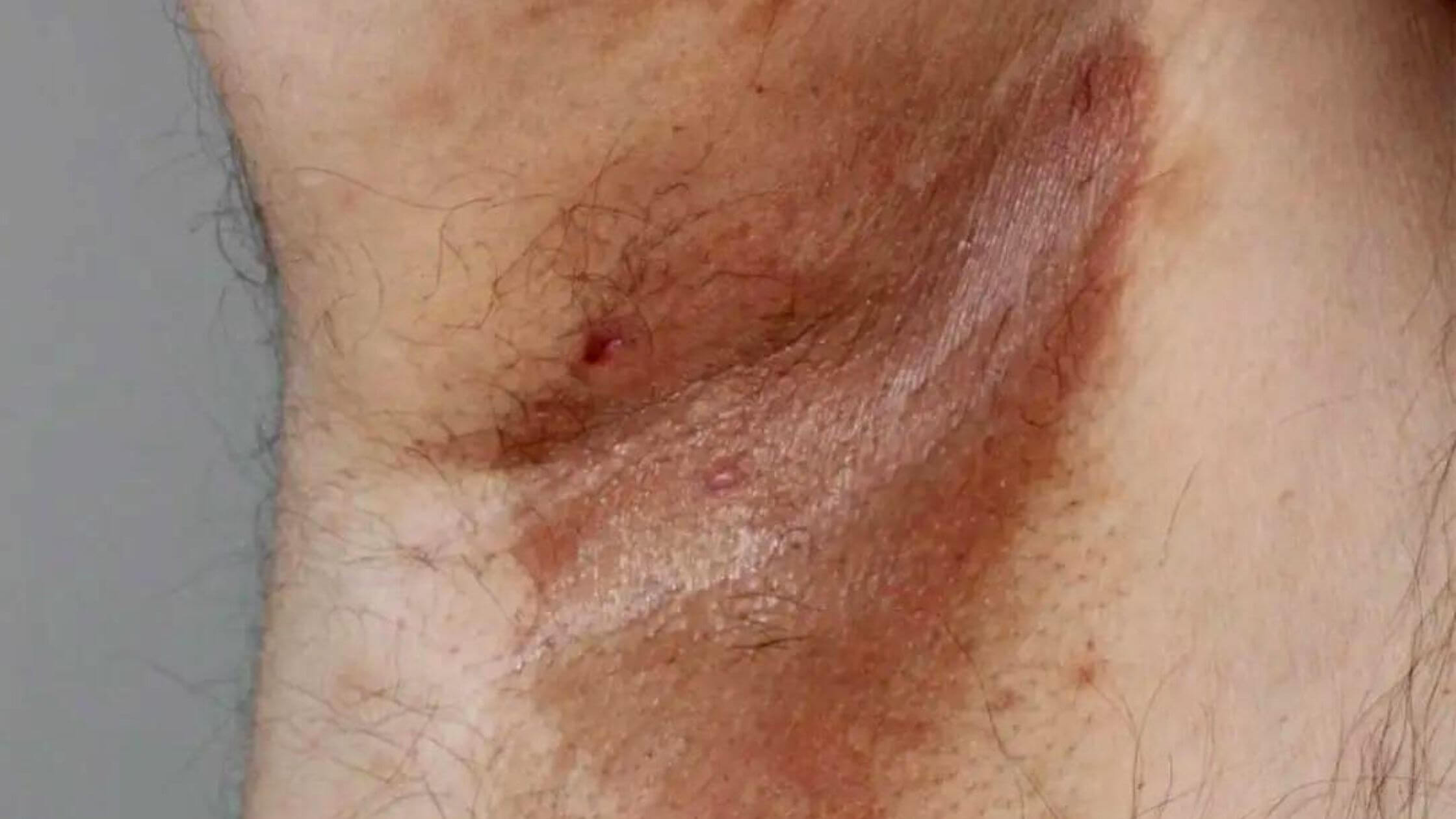
Erythrasma between the toes is found to have fissures and scaly skin. Erythrasma also appears in the skin folds under the breasts, between the buttocks, and around the navel. The bacteria causing erythrasma is normally found in the skin and grows in warm, moist areas.
Diagnosis of erythrasma begins with the physical examination of the affected parts. The doctor uses an ultraviolet lamp to check the infection. Under the lamp, parts affected by erythrasma will be in red or coral color. Once diagnosed, the treatment is done using oral antibiotics such as erythromycin.
Antibacterial creams or solutions are applied to the skin as part of the treatment. It may take two to four weeks for the treatment to work. Sometimes a combination of treatments is required to cure. Complications are rare in the case of erythrasma. In rare cases, it can cause septicemia, a serious blood infection.
MRSA Infections
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a dangerous bacterial infection. It is a serious infection as it is resistant to standard antibiotic treatment. It is caused by staph bacteria. The symptoms of MRSA can vary by the location of infection.
They typically include swelling, redness, pain, pus, and fever. If it gets serious, then there are chances for blood poisoning and shock. This infection can also be confused with a spider bite. The staph bacteria are found in the nose and on the skin and generally don’t cause any harm. MRSA infection occurs when they multiply uncontrollably.
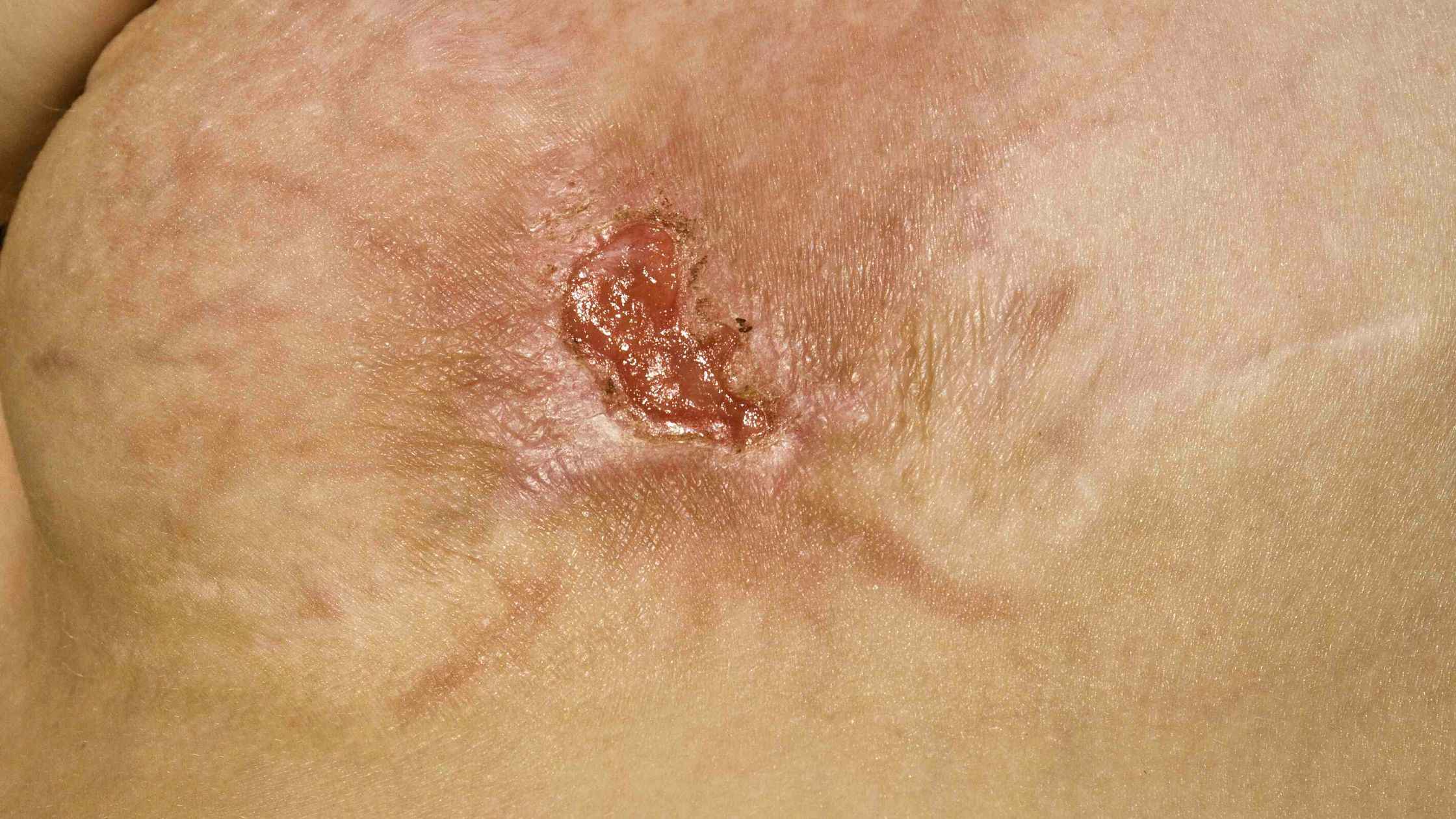
Infection generally enters through cuts in the skin. As it is very contagious, it can spread from an infected person on direct contact. Symptoms of MRSA infections include rash, headaches, muscle aches, chills, fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
Diagnosis of this condition is made through physical examinations. Samples are taken from the sites of infection. Treatment is done using antibiotics through IV. Treatment may have to be performed for a long time based on the severity of the infection. If the skin infection is large, then the doctor may perform an incision and drainage.
We have seen that bacterial rashes are caused by different bacteria. Most of them have similar symptoms and are difficult to tell apart. Most of the infections are not dangerous, but if left untreated they can become serious. Contact your skin specialist if you develop any of the above-mentioned symptoms.
