Health
Common Problems Affecting Ears: A Comprehensive Guide To Ear Problems

Our ears play a vital role in hearing and balance. Unfortunately, the ears are prone to various disorders that can impair these critical functions. Problems affecting ears range from temporary infections to permanent hearing loss.
This article will provide an overview of common ear conditions, their causes, symptoms, and effects. Understanding the wide range of ear problems that may arise can help prompt appropriate treatment to preserve ear health and hearing abilities.
Types of Ear Infections: Causes and Symptoms
Ear infections involve inflammation and infection of the outer, middle, or inner ear structures.
- Outer ear infections (otitis externa): It affects the ear canal. They are often called swimmer’s ear. Symptoms include pain, itching, and drainage. Risk factors are water exposure and ear trauma. Treatments include eardrops and avoiding irritation.
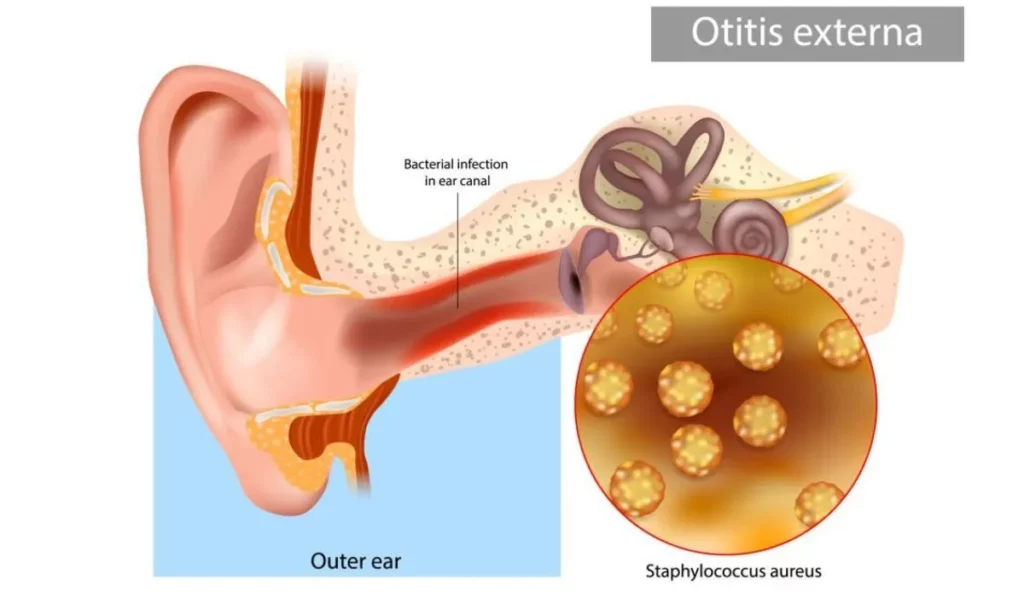
- Middle ear infections (otitis media): Occur behind the eardrum when fluid buildup gets infected. Symptoms are ear pain, fever, and muffled hearing. Causes are viruses, bacteria, and allergies. Treatments involve antibiotics, decongestants, and ear tubes to drain fluid.
- Inner ear infections (otitis interna): It affects the labyrinth and nerve pathways. Severe dizziness, ringing ears, nausea, and hearing loss occur. Upper respiratory infections increase risks. Treatments are antivirals, antibiotics, and anti-nausea medication.
Prompt diagnosis and treatment of ear infections prevents complications like chronic pain and hearing loss. Following medication instructions properly aids recovery.
Most Common Problems That Affecting Ears
Wax Accumulation
Ear wax protects the ear canal by trapping dirt and repelling water. However, excess wax buildup can cause blockage and hearing loss. Symptoms of problematic wax accumulation include earache, fullness, ringing, and coughing.
Seeking proper medical removal is safest as improper cleaning risks damage. Preventive measures include using earplugs when showering, avoiding the insertion of cotton swabs or objects into the ear, and applying drops to soften the wax.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus involves perceiving ringing or other phantom noises in the ears. Exposure to loud noises, age-related hearing loss, obstructions, head injuries, circulatory disorders, and neurologic conditions can trigger tinnitus.
Treatments aim to address underlying causes when possible, provide masking background noise, and teach coping strategies for managing symptoms. Supportive counseling helps those severely affected by chronic tinnitus. Research continues on optimal therapeutic approaches.
Hearing Loss
Various types of hearing loss exist, resulting from conductive disorders, inner ear damage, or auditory nerve impairment. Hearing loss has numerous causes including chronic noise exposure, genetics, aging, infections, autoimmune disease, birth defects, tumors, and trauma.
Management depends on the type and severity, ranging from hearing aids and implants to sign language training and lip reading for profound impairment. Protecting ear health helps maintain natural hearing abilities.
Vertigo and Dizziness
Vertigo involves a spinning sensation from inner ear balance disorders. Dizziness refers to similar feelings of being lightheaded or unsteady without room spinning. Potential causes include benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, labyrinthitis, Meniere’s disease, migraines, and medication side effects.
Diagnostic tests determine underlying reasons to guide appropriate interventions, which may include particle repositioning maneuvers, medications, hearing aids, surgery, and balance therapy.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction
The Eustachian tubes connect the middle ears to the throat, regulating ear pressure. Obstructions from allergies, colds, sinusitis or blockages can cause dysfunction, affecting hearing. Symptoms include muffled sounds, ear popping, fullness, pain, and dizziness.
Treatments aim to open the tubes through medications, posture techniques, swallowing exercises, CPAP masks, and surgery if conservative approaches fail. Keeping infections, allergies, and reflux under control helps prevent Eustachian tube dysfunction.
Seeking Professional Help
With many potential ear problems that can arise, periodic evaluations by ear specialists help identify any hearing or balance issues early. Otolaryngologists diagnose and treat a wide range of ear disorders. Audiologists assess hearing function.
For any persistent ear symptoms, getting examined promptly prevents unnecessary impairment and disability. Expert care optimizes outcomes when problems affecting ears develop.
Read More:- Steps For Disease Prevention And Healthy Living
Conclusion
Our ears are complex structures susceptible to various infections, injuries, pressure changes, and age-related issues. Catching ear disorders early and seeking appropriate expertise optimizes healing and function.
Protecting ear health through preventive actions reduces risks. Ongoing research provides hope for better treatments for chronic issues like tinnitus and hearing loss. Managing problems affecting ears properly helps preserve precious hearing and balance abilities.
