Health
Identifying The Signs Of Nerve Degeneration Recognizing Early Symptoms
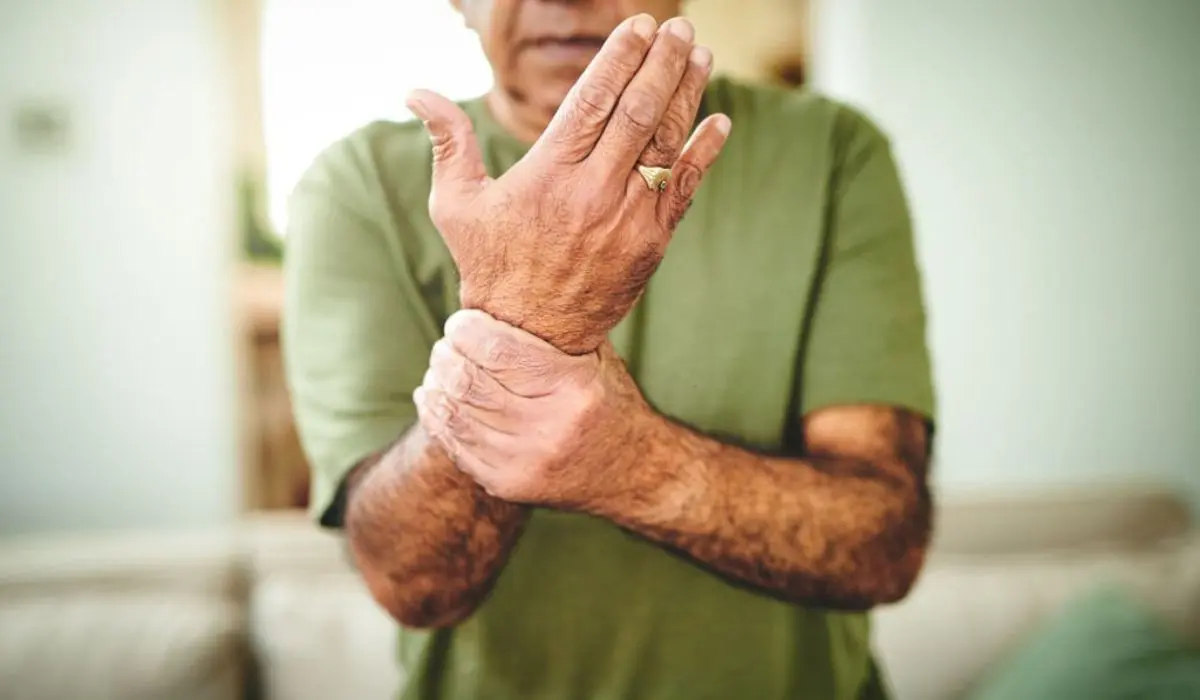
The human body is a complex system, and our nerves are essential messengers that send signals to and from the brain. But as we age, these nerves can begin to degenerate – causing physical and neurological issues.
Early signs of nerve degeneration are often subtle. Tingling or numbness in fingers or toes, difficulty balancing, or weakness in certain muscles may be symptoms. These can be ignored, but should not be.
Exercise and physical therapy can help to stimulate blood flow and regenerate nerves. Eating a healthy diet with vitamins and minerals, like B12 and omega-3 fatty acids, can also support nerve health. Lastly, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol can prevent further nerve damage.
It’s important to be aware of early signs of nerve degeneration and seek medical help. Exercise, nutrition, and avoiding bad habits are key for preserving nerve health and overall well-being.
Understanding Nerve Degeneration
Nerve degeneration is a complex condition impacting the nervous system, with diverse symptoms and complications. Knowing how it occurs is important to spot early signs. As it worsens, it affects one’s quality of life greatly. So, this understanding can be invaluable for individuals and healthcare professionals.
It usually starts with a gradual breakdown of the nerve fibers’ covering (myelin). This is called demyelination, which disrupts the normal flow of electrical impulses. Thus, those affected may suffer from weakness, numbness, tingling, lack of coordination/balance, muscle spasms, and pain.
Moreover, there are various causes of nerve degeneration. It can result from genetic factors or other medical issues like diabetes, autoimmune disorders (e.g. multiple sclerosis), infections (e.g. Lyme disease), or toxin exposure. To manage the condition, it is critical to identify its cause.
Furthermore, this is a field of ongoing research. Scientists are developing new diagnostic tools and therapies, such as neuroimaging and biomarker analysis, to diagnose and monitor nerve degeneration. They are also exploring treatments like gene therapies targeting mutations associated with certain types of nerve degeneration.
Common Signs And Symptoms
Nerve degeneration can manifest in a variety of ways, and it is essential to recognize the common signs and symptoms that may indicate its presence. By being aware of these indicators, individuals can seek early intervention and appropriate medical attention. Here are six key signs and symptoms to watch out for:
Diagnostic Tests
▪️ Electromyography (EMG)
Electromyography (EMG) is a test used to check the health of muscles and nerves. Electrodes, on the skin or in muscles, measure electrical activity. EMG can diagnose nerve, and muscle illnesses, and carpal tunnel syndrome.
Small electrical currents are used to stimulate muscles, and the signals are recorded. This test gives info about strength, nerve conduction, and any issues or injuries. EMG is often done with other tests, to get a full understanding of the condition.
EMG helps to plan treatments for neurological disorders. It gives healthcare providers the knowledge to decide the best course of action for patients.
▪️ Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS) measure electrical activity in nerves to evaluate health and performance. With small electrodes on the skin, NCS can reveal if any nerve damage is present. This non-invasive technique helps diagnose conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome and peripheral neuropathy.
Applying a low-level electrical current to specific nerves, the response is recorded with electrodes. The speed and intensity of the signals are measured. This data provides information about nerve communication and blockages. NCS can detect areas of nerve damage, recognize the seriousness of the condition, and assist with treatment planning.
NCS also examines muscle reaction to stimulation. This allows healthcare professionals to differentiate between nerve and muscle disorders. Knowing the source of symptoms like weakness or numbness, appropriate treatment options can be explored.
Technology has improved the accuracy and dependability of Nerve Conduction Studies over the years. They are vital in diagnosing neurological disorders, helping with early intervention, and improving patient outcomes. Regular use of this diagnostic tool has greatly increased medical understanding of nerve health and functionality.
▪️ Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a powerful diagnostic tool. It uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. MRI provides very clear and precise pictures. This helps healthcare professionals to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions.
The basis of MRI is the behavior of hydrogen atoms when they are exposed to the magnetic field. These atoms line up with the field and emit signals when they return to their original state after being subjected to radio waves.
The signals are then detected and processed by a computer. This generates detailed images in different planes so a comprehensive examination of the area can be done.
MRI is special in that it produces images without using ionizing radiation, such as X-rays or CT scans. This makes it ideal for imaging sensitive tissues like the brain, spinal cord, and reproductive organs. Additionally, MRI can give info on blood flow. It is helpful for detecting tumors or blocked blood vessels.
Conclusion
Acknowledge any pain, tingling, numbness, or weakness that persists or worsens. Don’t dismiss these symptoms, as they could be nerve damage. Look out for a decline in motor skills or coordination.
If having difficulty with fine movements, like buttoning a shirt or holding a pen, see a healthcare professional. Heightened sensitivity to touch, cold, or heat, or a diminished sense of touch could also signify nerve damage.
Consult with a neurologist who specializes in diagnosing and treating nerve damage. They can conduct tests such as EMG or nerve conduction studies.
