Health
Type 2 Diabetes In Women: Signs and Complications
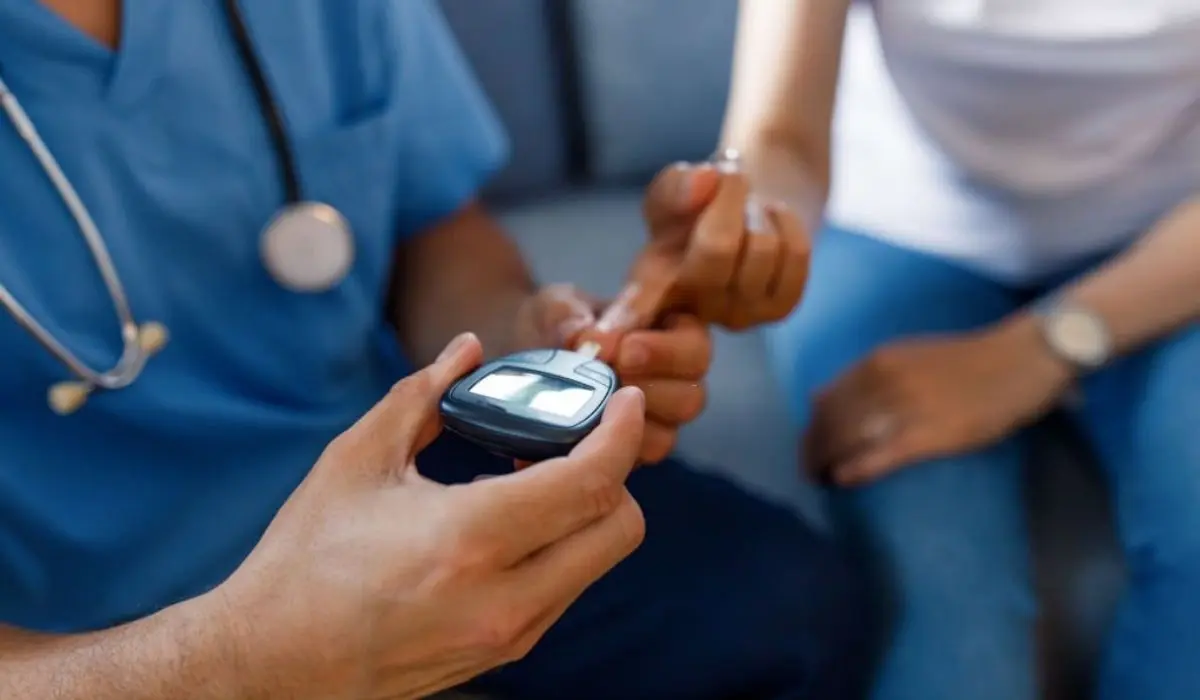

Type 2 Diabetes is a growing issue for women worldwide. It’s a metabolic disorder caused by the body’s inability to use insulin or produce enough of it. Common signs include frequent urination, increased thirst, weight loss, and fatigue. Regular tests are key for early detection of warning signs.
Complications can be severe and life-threatening if left unmanaged. Women with Type 2 Diabetes have an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney damage, nerve damage, diabetic retinopathy, and pregnancy complications. Age and ethnicity add to the uniqueness of complications. Healthcare providers should tailor treatments to each patient’s needs.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a common chronic condition for many women. The body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough of it. Without enough insulin, glucose can’t enter cells for energy, leading to high sugar levels and bad health problems.
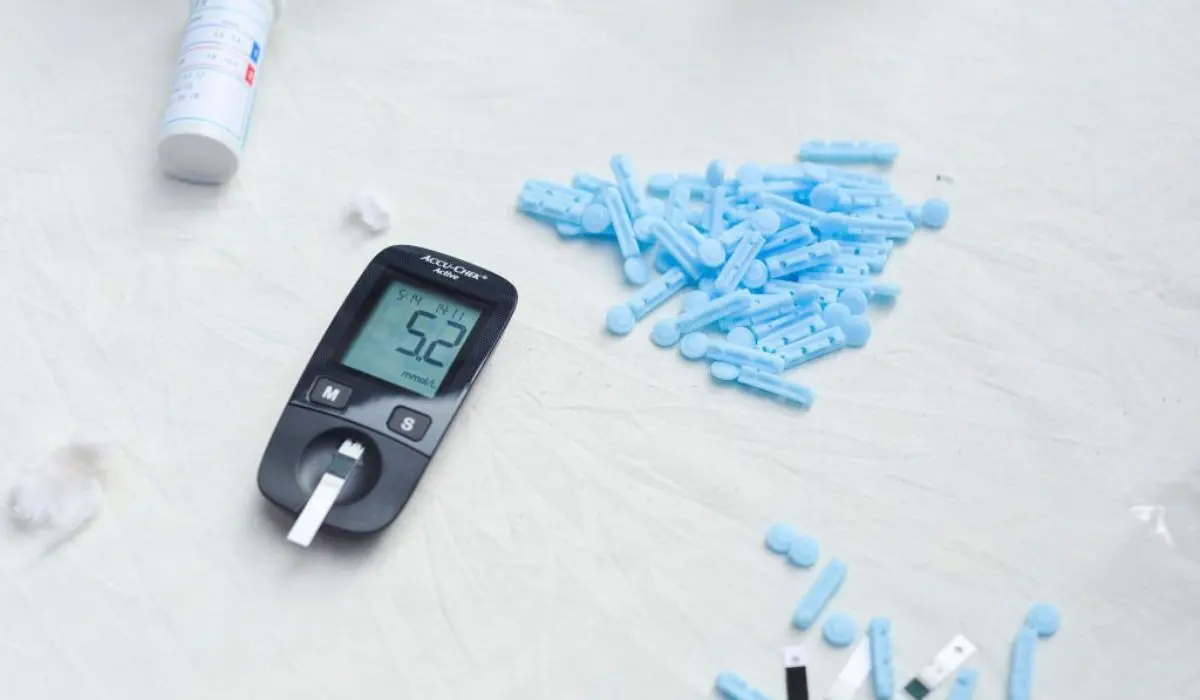
Managing type 2 diabetes needs lots of care. Regular exercise, a diet low in sugar and carbs, and weight control are key. Monitor blood sugar and take medication as advised by healthcare professionals.
If type 2 diabetes is not managed, complications can occur. Damage to parts of the body like eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart can happen over time. This can cause vision loss, kidney disease, pain or numbness in extremities, and an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Signs And Symptoms Of Type 2 Diabetes
▪️ Increased thirst and frequent urination
Insulin resistance often causes Type 2 Diabetes. Insulin helps sugar enter cells and give us energy. But, when this process is disrupted, blood sugar levels go up!
Thirsty often? Going to the loo a lot? Unexplained weight loss or gain? Blurry vision? Do wounds heal slowly? Infections often? These are all signs of Type 2 Diabetes!
▪️ Fatigue and weakness
High blood sugar levels are the cause of fatigue and weakness in Type 2 Diabetes. Cells become resistant to insulin, so there’s not enough glucose uptake. When the body can’t get enough energy, it’s reflected in tiredness and general weakness.
▪️ Unintentional weight loss
Unexplained weight loss may come with other signs, such as thirst and peeing more. This happens ’cause the body tries to get rid of extra glucose through urine, causing dehydration and a feeling of always being thirsty. People may also be tired since the body can’t turn glucose into usable energy properly.
To treat unintentional weight loss caused by type 2 diabetes, it’s important to have the right blood sugar levels. This can be done with medicine, lifestyle changes, and diet. You must keep an eye on your blood sugar levels to make sure they’re in the right range.
▪️ Slow healing of wounds
People with type 2 diabetes may experience slower healing of wounds. This is because their body can’t regulate blood sugar levels, which can damage blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the affected area.
White blood cells, which fight infection, may not work properly either. And, nerve damage from diabetes can cause decreased sensation in areas with wounds, so individuals may not notice them until they become severe.
▪️ Blurred vision
Diabetes can wreak havoc on the blood vessels in your eyes, leading to changes in their structure and function – which may result in blurry vision. This may come and go throughout the day, and if left unmanaged, can progress to more serious problems like diabetic retinopathy.
People living with this condition should get regular eye exams to monitor any vision changes and detect eye diseases quickly. Prompt medical advice can make a huge difference in maintaining good eye health with type 2 diabetes.
Complications Of Type 2 Diabetes
To better understand the complications of type 2 diabetes, dive into the various areas affected by this condition. Explore heart disease and stroke, kidney damage, nerve damage, eye problems, and foot problems as potential challenges that individuals with type 2 diabetes may face.
➜ Heart disease and stroke
Atherosclerosis is when fatty deposits build up in the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow. This can lead to the formation of clots blocking blood to vital organs like the heart and brain.
People with type 2 diabetes are 2-4 times more likely to have a heart attack or stroke. This is because of things like high blood pressure, bad cholesterol, obesity, and not exercising enough.
➜ Kidney damage
The kidneys are key to good health, purifying the blood and eliminating waste. But when someone has Type 2 diabetes, glucose levels can impair blood vessels and affect kidney performance. Over time, this can cause kidney damage.
One of the early signs is proteinuria. That’s when the kidneys can’t retain protein, resulting in a lot of protein in the urine. Other effects are swelling in legs and ankles from fluid retention, plus higher blood pressure, and worsening kidney damage.
➜ Nerve damage
Diabetic neuropathy, a type 2 diabetes complication, can be severe and long-lasting. It occurs when high blood sugar damages the nerves. It can affect the feet/legs, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. In some cases, it can lead to more serious issues such as infections and ulcers.
Not everyone with type 2 diabetes will develop nerve damage. Factors that play a role include long-term control of blood sugar levels and proper management of the condition. Check-ups and medical advice are key for preventing and managing this complication.
➜ Eye problems
Type 2 Diabetes can cause serious damage to various parts of the body, especially the eyes. It can lead to vision loss if not managed properly. People with Type 2 Diabetes are prone to developing a condition called diabetic retinopathy, as high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina.
This progresses slowly and often does not show symptoms until it reaches advanced stages. Hence, regular eye exams are essential for early detection and treatment.
Moreover, people with Type 2 Diabetes are at an increased risk of developing other conditions like cataracts and glaucoma. Cataracts cause clouding of the lens in the eye, leading to blurred vision. Meanwhile, glaucoma damages the optic nerve and can cause permanent vision loss unless treated.
➜ Foot problems
Foot problems are a major issue for type 2 diabetes, including nerve damage, circulation issues, ulcers, corns, and calluses. Plus, fungal infections such as athlete’s foot can occur.
It’s vital for people with type 2 diabetes to look after their feet. Wear the right shoes, inspect your feet regularly, and keep them clean.
Prevention And Management Of Type 2 Diabetes
✔️ Healthy eating and regular physical activity
Eating healthy and being active can do wonders for your health beyond managing blood sugar! Adopting a lifestyle focused on these habits can prevent type 2 diabetes, increase energy and mood, and improve cardiovascular health.
✔️ Monitoring blood sugar levels
Managing Type 2 Diabetes requires monitoring blood sugar levels. Through a variety of methods, such as a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring systems, individuals can collect data and make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication.
✔️ Taking prescribed medications
Medications are vital for managing type 2 diabetes. They help lower blood pressure and cholesterol. This lowers the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Medication adherence is important for good glucose control.
To ensure this, integrate it into daily routines. Set reminders, use pill organizers, or use apps. Get support from healthcare providers and loved ones. Regular check-ups and screenings show you care about your health.
✔️ Regular check-ups and screenings
Regular check-ups are important for monitoring blood sugar levels and assessing overall health. They can spot potential complications related to diabetes, plus help adjust medications.
These check-ups also provide education and support regarding lifestyle modifications, diet, exercise, and medication adherence. Furthermore, they help build trust and open communication between patients and healthcare professionals.
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes in women should not be taken lightly. Its impacts are vast. Women must be aware of symptoms and seek a diagnosis. They must take steps to manage their health. Early detection plays a big role in preventing further complications.
Such as frequent urination, thirst, weight loss, and fatigue. Prompt medical intervention helps to limit the risk of more serious issues like heart disease, kidney, and nerve damage.
Women with type 2 diabetes need tailored management plans. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause glycemic control problems. PCOS, which is linked with insulin resistance, increases the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is a challenge for women’s health. With awareness and proactive action, it can be managed. Women must stay alert to signs and complications. This will help them lead healthier lives and reduce risks to their well-being.
